flowchart LR
Data --> Model
subgraph Model
direction TB
Preprocessing --> Method
Method --> Postprocessing
end
Model --> Prediction
6 Workflows: Connecting the parts
Initially, one might think of a model as just the specific method or algorithm, for example a linear regression or a random forest; it is however more than that. Before we train the algorithm, we may need to preprocess the data. To name a few examples, we may want to
- normalize the data,
- transform into principal components,
- select a subset of features based on their properties,
- and/or handle missing values.
In many cases, these steps depend on the training data as much as the trained method itself. If we want to predict new data, they also need to pass the same preprocessing steps before the trained algorithm can be applied. It is therefore better to consider a model as being a combination of preprocessing and method. We may take this a step further and consider postprocessing the outcome/prediction of the trained method. The following graph summarizes the modeling workflow. The data is first preprocessed, then the method is applied, and finally the predictions are postprocessed. Preprocessing, method, and postprocessing together make up the model and can all depend on the training data.
6.1 Workflows in tidymodels
As we’ve seen, training a model is a multi-step process. We need to consider:
- defining the model
- training and validating the model
- deploying the model
Figure 7.1 summarizes this modeling workflow and shows how the individual steps are implemented in the tidymodels framework.
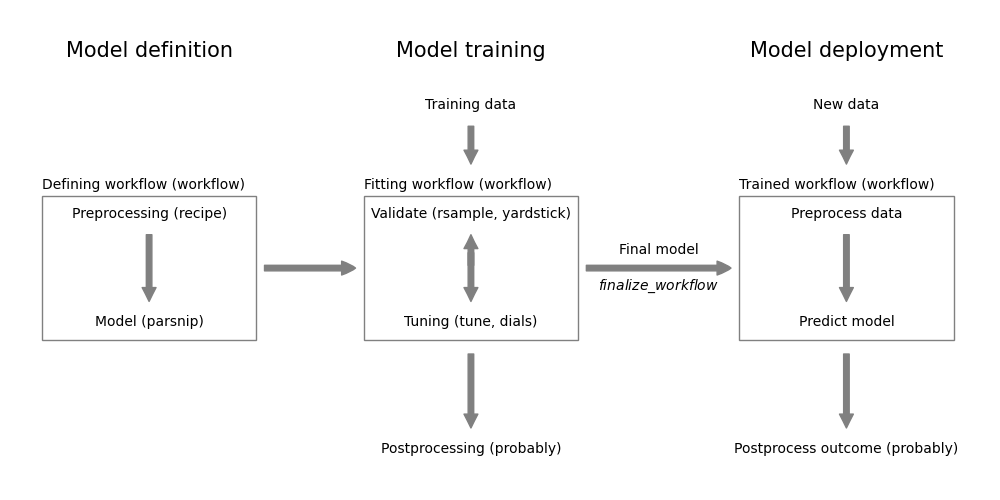
The left column covers the model definition part. A complete model definition requires:
- Preprocessing (
recipepackage - see Chapter 7) - Model specification (
parsnippackage - see Chapter 8, Chapter 10) - Postprocessing (
probably- see Section 11.1.2)
The workflow package from tidymodels, allows to combine the first two steps into a single workflow object. The workflow object can then be used to train and validate the model. Only the preprocessing and model specification can be included in the workflow at the moment. While the postprocessing step should be part of the full model process, the workflow package doesn’t support it. For now, the postprocessing step has to be done separately. For example, we will see in Section 11.1.2 how the probably package can be used to define a threshold for binary classification models.
The workflow package is also able to orchestrate the model tuning and validation. It involves:
- Model tuning (
tunepackage - see Chapter 14) - Model validation (
rsample,yardstickpackages - see Chapter 12, Chapter 13) - Tune postprocessing (
probablypackage - see Chapter 14)
The objective of model tuning is to find the best model parameters. This can include the model hyperparameters (e.g. the number of trees in a random forest) and the preprocessing parameters (e.g. the number of principal components in a PCA). The tune package allows to define potential values and combinations of these parameters. This combined with the validation strategy defined using the rsample package, allows tune to examine the performance of different models and select the “best” one. The performance is measured using the various metrics provided by the yardstick package.
At the end of the model training step, we end up with a final trained workflow for deployment. For now, this means
- predict new data using the final model by:
- preprocessing the new data using the (tuned) preprocessing steps
- predicting with the (tuned) model
- if applicable, postprocessing the predictions (e.g. applying a threshold for the predicted class probabilities)
6.2 Workflow example
The following chapters covers the components of workflows in more detail. This can make it difficult to see the big picture. You can find complete workflows in the examples part.
- Chapter 25 covers preprocessing, model definition, tuning using cross-validation, finalizing the tuned model, and validating with a holdout set.
- Chapter 26 covers preprocessing, model definition, tuning using cross-validation, threshold selection using cross-validation results of the best mdoel, and prediction with the tuned model and threshold.
6.3 Models vs. workflows
It may initially be confusing to have a second way to build models. However, there is consistency between using both. As can be seen from the following table, the two approaches are similar and only differ in the way the models and the formula are specified.| Task | Model | Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Specification |
model <- linear_reg() |
rec_definition <- recipe() %>%
add_formula(formula)
wf <- workflow() %>%
add_model(linear_reg()) %>%
add_recipe(rec_definition)
|
| Validation |
result_cv <- model %>%
fit_resamples(formula, resamples)
|
result_cv <- wf %>%
fit_resamples(resamples)
|
| Model fit |
fitted_model <- model %>%
fit(formula, trainData)
|
fitted_model <- wf %>%
fit(trainData)
|
| Prediction |
pred <- fitted_model %>%
predict(new_data=newdata)
|
pred <- fitted_model %>%
predict(new_data=newdata)
|
| Augmenting a dataset |
aug_data <- fitted_model %>%
augment(new_data=newdata)
|
aug_data <- fitted_model %>%
augment(new_data=newdata)
|
As we will see in Chapter 7 and Chapter 14, workflows are required to incorporate preprocessing into the model building process and to tune model parameters. It is therefore best, to use workflows and use simple models only when absolutely necessary.
- Take the short datacamp course at https://app.datacamp.com/learn/courses/modeling-with-tidymodels-in-r
- Go to https://workflows.tidymodels.org/ to learn more about the
workflowspackage - The workflowsets package allows to combine multiple workflows into a single object. This is useful when you want to compare multiple preprocessing steps and/or multiple models at the same time. We will not cover this package in this class.